Written by Wesley Chee, Ergonomist at AnjouHealth and Director & Chief Sports Physiotherapist at Physio & Sole Clinic
Many workplace injuries do not occur suddenly in accidents. Instead, they develop gradually from everyday work practices, prolonged sitting, poorly positioned screens, repetitive keyboard use, and limited movement throughout the workday.
In Singapore’s predominantly office-based work environment, these issues are increasingly common. Ergonomic risk assessment plays a critical role in identifying such risks early, helping organisations prevent injuries, protect employee wellbeing, and maintain productivity.
This article explains what ergonomic risk assessment is, why it matters, what it includes, and how it supports safer workplaces in Singapore.
The Problem: Ergonomic Risks Are Common but Often Overlooked

What are ergonomic risks in the workplace?
Ergonomic risks are workplace factors that place physical strain on the body due to how work is designed or performed. In office environments, common ergonomic risks include:
- Poor workstation setup
- Prolonged sitting or static postures
- Repetitive movements such as typing or mouse use
- Awkward neck, shoulder, wrist, or back positions
- Inadequate desk, chair, or screen height
Because these risks do not usually cause immediate injury, they are often dismissed as minor discomfort rather than recognised as early warning signs of developing musculoskeletal issues.
Why Ergonomic Risks Become a Serious Workplace Issue

Why is ergonomic risk assessment important?
Ergonomic risks are cumulative. When exposure continues over time without intervention, small strains can develop into musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) affecting the neck, shoulders, wrists, or lower back.
Without ergonomic risk assessment:
- Employee discomfort may progress into chronic pain
- Focus and productivity can decline
- Absenteeism and medical-related costs may increase
- Organisations face a greater risk of work-related injury claims
- Overall standards of living are reduced
In Singapore, where many employees spend long hours at desks or on laptops, both in offices and at home, managing ergonomic risks is essential for long-term workforce sustainability.
The Solution: Ergonomic Risk Assessment
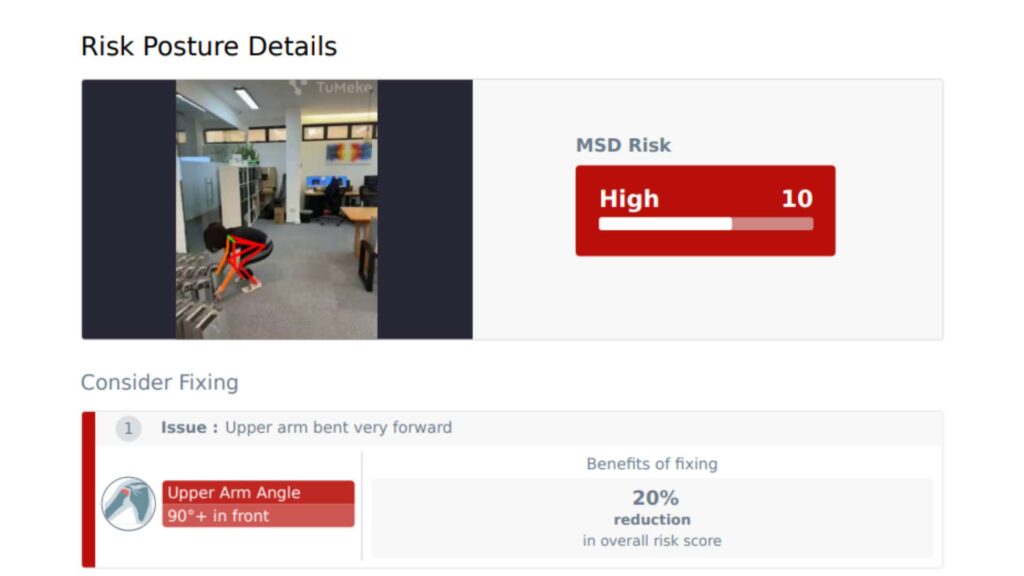
What is an ergonomic risk assessment?
An ergonomic risk assessment is a structured process used to identify, evaluate, and manage ergonomic risks in the workplace.
Rather than focusing only on furniture, a proper ergonomic risk assessment considers:
- The employee’s workstation setup
- Task demands and work duration
- Posture and movement patterns
- Work habits, breaks, and variability
The objective is to ensure that the work environment is designed to support the worker, reducing strain and injury risk.
What are the 5 main ergonomic risk factors?
Ergonomic risk assessments commonly evaluate five key risk factors:
- Repetition – Repeated movements such as typing or mouse use
- Force – Sustained muscle effort or tension
- Awkward posture – Poor alignment of the neck, shoulders, wrists, or back
- Duration – Long periods of sitting or static postures
- Contact stress – Pressure from hard surfaces like desk edges or armrests
When these factors occur together, the likelihood of discomfort and injury increases.
What are common ergonomic hazards in offices?
Common office ergonomic hazards include:
- Laptop-only setups without external keyboards or monitors
- Chairs without proper lumbar support
- Lack of foot support
- Screens positioned too low or too far away
- Incorrect desk height
- Prolonged sitting without movement breaks
These hazards are frequently linked to neck pain, shoulder tension, wrist strain, and lower back discomfort.
Who needs an ergonomic risk assessment?
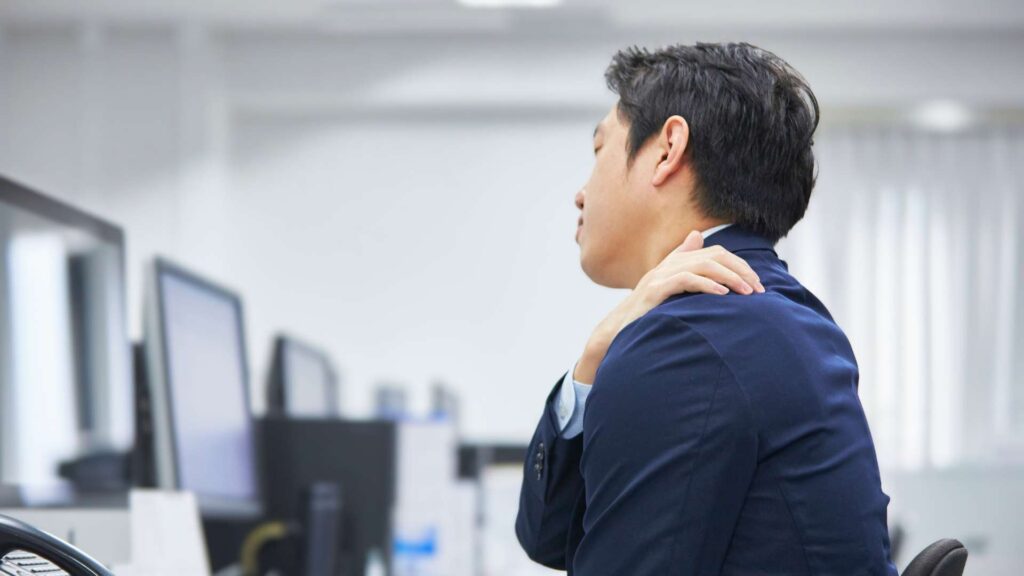

Ergonomic risk assessment is relevant for:
- Office-based employees
- HR professionals and people managers
- Work-from-home and hybrid workers
- Employees reporting discomfort or fatigue
- Employees returning from injury
- New hires adapting to new workstations
Importantly, ergonomic risk assessment is not only reactive. It is a preventive workplace safety measure that helps reduce injury risk before symptoms escalate.
When should an ergonomic risk assessment be done?
Organisations should consider ergonomic risk assessment when:
- Employees report pain, stiffness, or discomfort
- There is an increase in musculoskeletal-related sick leave
- New workstations, equipment, or office layouts are introduced
- Hybrid or remote work arrangements begin
- Employees return from injury or prolonged absence
Early intervention helps prevent minor ergonomic issues from becoming long-term health problems
What does an ergonomic risk assessment include?
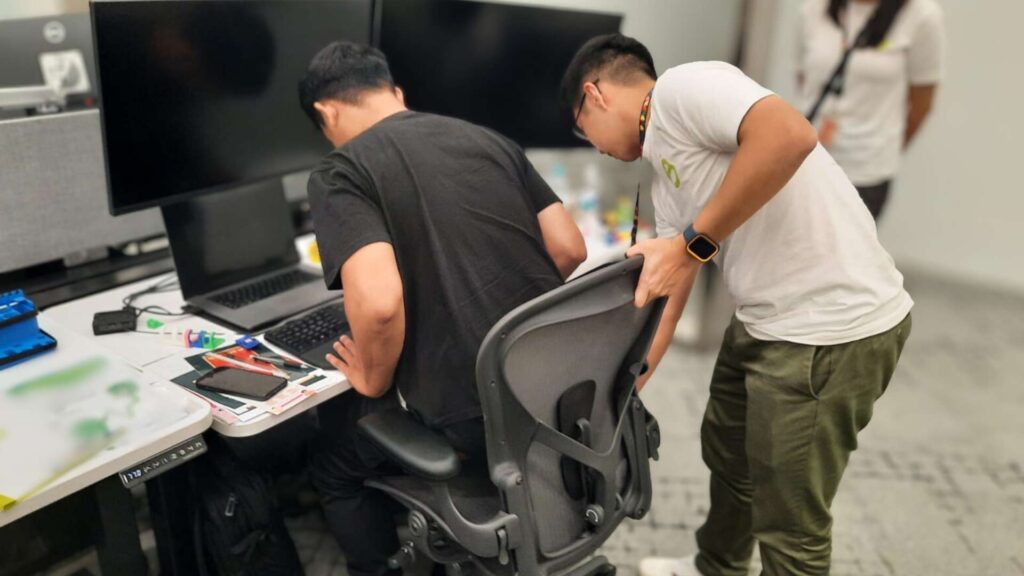

A typical ergonomic risk assessment includes:
- Observation of posture, movement, and work habits
- Discussion with the employee to understand comfort levels, symptoms, and concerns
- Review of workstation setup (chair, desk, screen, keyboard, mouse)
- Identification of ergonomic hazards and exposure risks
- On-the-spot workstation adjustments to improve safety and comfort
- Practical, actionable recommendations tailored to the individual
The focus is on realistic improvements that can be implemented within the workplace, rather than theoretical or generic advice.
What are the 5Rs of ergonomic risk assessment?
Ergonomic risk assessment often aligns with the 5 Rs of workplace risk assessment:
- Recognise ergonomic hazards
- Record who may be affected
- Risk-evaluate the severity and likelihood
- Reduce risks through controls and adjustments
- Review regularly to ensure effectiveness
This approach supports ongoing ergonomic risk management rather than one-off assessments.
How does ergonomic risk assessment prevent injuries?

Ergonomic risk assessment helps prevent injuries by:
- Identifying risks before symptoms worsen
- Improving posture and workstation alignment
- Reducing unnecessary muscle strain
- Encouraging healthier work habits and movement
- Supporting long-term musculoskeletal health
When applied consistently, ergonomic risk assessment shifts workplace safety from reactive treatment to preventive care.
Who conducts an ergonomic risk assessment?
In Singapore, ergonomic risk assessments are commonly conducted by:
- Ergonomic specialists
- Occupational health professionals
- Trained workplace safety practitioners
Professional assessments ensure that risks are properly identified and that recommendations align with workplace safety best practices.
Is ergonomic risk assessment required in Singapore?
While ergonomic risk assessment is not mandated for every individual workstation, employers in Singapore are required to identify and manage workplace risks under guidance from the Ministry of Manpower and the Workplace Safety and Health Council.Conducting ergonomic risk assessments demonstrates proactive compliance with workplace safety responsibilities, particularly for office-based environments.
Final Thoughts: A Preventive Approach to Workplace Ergonomics
Ergonomic risk assessment should be viewed as part of a broader workplace health and safety strategy, not merely a comfort initiative.
By identifying ergonomic risks early and addressing them systematically, organisations can protect employee wellbeing, support productivity, and reduce the likelihood of preventable injuries in the workplace.
Next Steps: Book a Call With Us

If your employees or colleagues are experiencing discomfort, work arrangements have changed, or workstations have not been reviewed recently, an ergonomic risk assessment in Singapore may be timely.
A structured ergonomic risk assessment provides clarity, practical recommendations, and long-term benefits for both employees and organisations.
To explore whether an ergonomic risk assessment is suitable for your workplace, book a call with our team.
We’ll help you understand your ergonomic risks, workplace responsibilities, and the practical steps needed to create a safer, healthier work environment.